Mammalian Eye on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Accessed October 25, 2006. The choroid contains
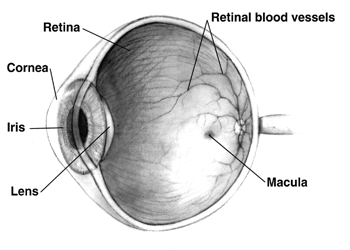 The mammalian eye can also be divided into two main segments: the
The mammalian eye can also be divided into two main segments: the
Mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
normally have a pair of eyes. Although mammalian vision is not so excellent as bird vision
Vision is the most important sense for birds, since good eyesight is essential for safe flight. Birds have a number of adaptations which give visual acuity superior to that of other vertebrate groups; a pigeon has been described as "two eyes with ...
, it is at least dichromatic for most of mammalian species, with certain families (such as Hominidae
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the ea ...
) possessing a trichromatic
Trichromacy or trichromatism is the possessing of three independent channels for conveying color information, derived from the three different types of cone cells in the eye. Organisms with trichromacy are called trichromats.
The normal expl ...
color perception.
The dimensions
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordina ...
of the eyeball vary only 1–2 mm among humans. The vertical axis is 24 mm; the transverse being larger. At birth it is generally 16–17 mm, enlarging to 22.5–23 mm by three years of age. Between then and age 13 the eye attains its mature size. It weighs 7.5 grams and its volume is roughly 6.5 ml. Along a line through the nodal (central) point of the eye is the optic axis, which is slightly five degrees toward the nose from the visual axis (i.e., that going towards the focused point to the fovea).
Three layers
The structure of themammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
ian eye has a laminar organization
A laminar organization describes the way certain tissues, such as bone membrane, skin, or brain tissues, are arranged in layers.
Types Embryo
The earliest forms of laminar organization are shown in the diploblastic and triploblastic formation ...
that can be divided into three main layers or ''tunics'' whose names reflect their basic functions: the fibrous tunic, the vascular tunic, and the nervous tunic.
* The fibrous tunic, also known as the ''tunica fibrosa oculi'', is the outer layer of the eyeball consisting of the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power ...
and sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the human eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber. In humans, and som ...
.Cline D; Hofstetter HW; Griffin JR. ''Dictionary of Visual Science''. 4th ed. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston 1997. The sclera gives the eye most of its white color. It consists of dense connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
filled with the protein collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
to both protect the inner components of the eye and maintain its shape.
* The vascular tunic, also known as the ''tunica vasculosa oculi'' or the "uvea", is the middle vascularized layer which includes the iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
, ciliary body
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliar ...
, and choroid
The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye, and contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear ...
.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990."Medline Encyclopedia: Eye."Accessed October 25, 2006. The choroid contains
blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s that supply the retinal cells with necessary oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
and remove the waste products of respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
. The choroid gives the inner eye a dark color, which prevents disruptive reflections within the eye. The iris is seen rather than the cornea when looking straight in one's eye due to the latter's transparency, the pupil
The pupil is a black hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. (1990) ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company. It appears black ...
(central aperture of iris) is black because there is no light reflected out of the interior eye. If an ophthalmoscope is used, one can see the fundus, as well as vessels (which supply additional blood flow to the retina) especially those crossing the optic disk—the point where the optic nerve fibers depart from the eyeball—among others"eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles ...
5 Apr. 2008
* The nervous tunic, also known as the ''tunica nervosa oculi'', is the inner sensory layer which includes the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
.
** Contributing to vision, the retina contains the photosensitive rod and cone cell
Cone cells, or cones, are photoreceptor cells in the retinas of vertebrate eyes including the human eye. They respond differently to light of different wavelengths, and the combination of their responses is responsible for color vision. Cone ...
s and associated neurons. To maximise vision and light absorption, the retina is a relatively smooth (but curved) layer. It has two points at which it is different; the fovea
Fovea () (Latin for "pit"; plural foveae ) is a term in anatomy. It refers to a pit or depression in a structure.
Human anatomy
*Fovea centralis of the retina
* Fovea buccalis or Dimple
* Fovea of the femoral head
* Trochlear fovea of the fr ...
and optic disc
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. Because there are no rods or cones overlying the optic disc, it corresponds to a small blind spot in each eye.
The ganglion cell axons form the ...
. The fovea is a dip in the retina directly opposite the lens, which is densely packed with cone cells. It is largely responsible for color vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
in humans, and enables high acuity, such as is necessary in reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of Letter (alphabet), letters, symbols, etc., especially by Visual perception, sight or Somatosensory system, touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process invo ...
. The optic disc, sometimes referred to as the anatomical blind spot, is a point on the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
where the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
pierces the retina to connect to the nerve cells on its inside. No photosensitive cells exist at this point, it is thus " blind". Continuous with the retina are the ciliary epithelium and the posterior epithelium of the iris.
** In addition to the rods and cones, a small proportion (about 1-2% in humans) of the ganglion cells in the retina are themselves photosensitive through the pigment melanopsin. They are generally most excitable by blue light, about 470–485 nm. Their information is sent to the SCN (suprachiasmatic nuclei), not to the visual center, through the retinohypothalamic tract
In neuroanatomy, the retinohypothalamic tract (RHT) is a photic neural input pathway involved in the circadian rhythms of mammals. The origin of the retinohypothalamic tract is the intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGC), whi ...
which is formed as melanopsin-sensitive axons exit the optic nerve. It is primarily these light signals which regulate circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogeno ...
s in mammals and several other animals. Many, but not all, totally blind individuals have their circadian rhythms adjusted daily in this way. The ipRGCs
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence ...
have other functions as well, such as signaling the need for changing the diameter of the pupil in changing light conditions.
Anterior and posterior segments
 The mammalian eye can also be divided into two main segments: the
The mammalian eye can also be divided into two main segments: the anterior segment
The anterior segment or anterior cavity is the front third of the eye that includes the structures in front of the vitreous humour: the cornea, iris, ciliary body, and lens.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesvill ...
and the posterior segment
The posterior segment or posterior cavity is the back two-thirds of the eye that includes the anterior hyaloid membrane and all of the optical structures behind it: the vitreous humor, retina, choroid, and optic nerve. of the eye that includes the structures in front of the
Cantabrian Institute of Ophthalmology. Within the anterior segment are two fluid-filled spaces: * the
 The purpose of the optics of the mammalian eye is to bring a clear image of the visual world onto the retina. Because of limited
The purpose of the optics of the mammalian eye is to bring a clear image of the visual world onto the retina. Because of limited
vitreous humour
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor ...
: the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power ...
, iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
, ciliary body
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliar ...
, and lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), ...
."Departments. Anterior segment."Cantabrian Institute of Ophthalmology. Within the anterior segment are two fluid-filled spaces: * the
anterior chamber
The anterior chamber ( AC) is the aqueous humor-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface, the endothelium. Hyphema, anterior uveitis and glaucoma are three main pathologies in this area. In hyphema, blood f ...
between the posterior surface of the cornea (i.e. the corneal endothelium
The corneal endothelium is a single layer of endothelial cells on the inner surface of the cornea. It faces the chamber formed between the cornea and the iris.
The corneal endothelium are specialized, flattened, mitochondria-rich cells that li ...
) and the iris.
* the posterior chamber
The posterior chamber is a narrow space behind the peripheral part of the iris, and in front of the suspensory ligament of the lens and the ciliary processes. The posterior chamber consists of small space directly posterior to the iris but anterio ...
between the iris and the front face of the vitreous.
Aqueous humor
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the posteri ...
fills these spaces within the anterior segment and provides nutrients to the surrounding structures.
Some ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgery, surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Followin ...
s specialize in the treatment and management of anterior segment disorders and diseases.
The posterior segment is the back five-sixths of the eye that includes the anterior hyaloid membrane
The vitreous membrane (or hyaloid membrane or vitreous cortex) is a layer of collagen separating the vitreous humour from the rest of the eye. At least two parts have been identified anatomically. The posterior hyaloid membrane separates the rea ...
and all of the optical structures behind it: the vitreous humor
The vitreous body (''vitreous'' meaning "glass-like"; , ) is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball (the vitreous chamber) in humans and other vertebrates. It is often referred to as the vitreous humor ...
, retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
, choroid
The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is a part of the uvea, the vascular layer of the eye, and contains connective tissues, and lies between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear ...
, and optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
.
The radii of the anterior and posterior sections are 8 mm and 12 mm, respectively. The point of junction is called the limbus.
On the other side of the lens is the second humour, the aqueous humour
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the posterio ...
, which is bounded on all sides by the lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), ...
, the ciliary body
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliar ...
, suspensory ligaments and by the retina. It lets light through without refraction, helps maintain the shape of the eye and suspends the delicate lens. In some animals, the retina contains a reflective layer (the tapetum lucidum
The ''tapetum lucidum'' ( ; ; ) is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrates and some other animals. Lying immediately behind the retina, it is a retroreflector. It reflects visible light back through the retina, increasing the light a ...
) which increases the amount of light each photosensitive cell perceives, allowing the animal to see better under low light conditions.
The tapetum lucidum, in animals that have it, can produce eyeshine
The ''tapetum lucidum'' ( ; ; ) is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrates and some other animals. Lying immediately behind the retina, it is a retroreflector. It reflects visible light back through the retina, increasing the light a ...
, for example as seen in cat eyes at night. Red-eye effect
The red-eye effect in photography is the common appearance of red pupils in color photographs of the eyes of humans and several other animals. It occurs when using a photographic flash that is very close to the camera lens (as with most compac ...
, a reflection of red blood vessels, appears in the eyes of humans and other animals that have no tapetum lucidum, hence no eyeshine, and rarely in animals that have a tapetum lucidum. The red-eye effect is a photographic effect, not seen in nature.
Some ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgery, surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Followin ...
s specialise in this segment.
Extraocular anatomy
Lying over the sclera and the interior of the eyelids is a transparent membrane called theconjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium ...
. It helps lubricate the eye by producing mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is ...
and tears
Tears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands (tear gland) found in the eyes of all land mammals. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of ...
. It also contributes to immune surveillance and helps to prevent the entrance of microbes
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
into the eye.
In many animals, including humans, eyelid
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eyel ...
s wipe the eye and prevent dehydration. They spread tears
Tears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands (tear gland) found in the eyes of all land mammals. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of ...
on the eyes, which contains substances which help fight bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of ...
as part of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
. Some species have a nictitating membrane
The nictitating membrane (from Latin '' nictare'', to blink) is a transparent or translucent third eyelid present in some animals that can be drawn across the eye from the medial canthus to protect and moisten it while maintaining vision. All ...
for further protection.
Some aquatic animals have a second eyelid in each eye which refracts the light and helps them see clearly both above and below water. Most creatures will automatically react to a threat to its eyes (such as an object moving straight at the eye, or a bright light) by covering the eyes, and/or by turning the eyes away from the threat. Blinking the eyes is, of course, also a reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
.
In many animals, including humans, eyelash
An eyelash (also called lash) (Latin: ''Cilia'') is one of the hairs that grows at the edge of the eyelids. It grows in one layer on the edge of the upper and lower eyelids. Eyelashes protect the eye from debris, dust, and small particles and p ...
es prevent fine particles from entering the eye. Fine particles can be bacteria, but also simple dust which can cause irritation of the eye, and lead to tears and subsequent blurred vision.
In many species, the eyes are inset in the portion of the skull known as the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a p ...
s or eyesockets. This placement of the eyes helps to protect them from injury. For some, the focal fields of the two eyes overlap, providing them with binocular vision
In biology, binocular vision is a type of vision in which an animal has two eyes capable of facing the same direction to perceive a single three-dimensional image of its surroundings. Binocular vision does not typically refer to vision where an ...
. Although most animals have some degree of binocular vision the amount of overlap largely depends on behavioural requirements.
In humans, the eyebrow
An eyebrow is an area of short hairs above each eye that follows the shape of the lower margin of the brow ridges of some mammals. In humans, eyebrows serve two main functions: first, communication through facial expression, and second, preven ...
s redirect flowing substances (such as rainwater or sweat) away from the eye.
Function of the mammalian eye
The structure of the mammalian eye owes itself completely to the task of focusinglight
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 tera ...
onto the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
. This light causes chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
changes in the photosensitive Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicit ...
cells of the retina, the products of which trigger nerve impulse
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, ...
s which travel to the brain.
In the human eye, light enters the pupil and is focused on the retina by the lens. Light-sensitive nerve cells called rods (for brightness), cones
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines conn ...
(for color) and non-imaging ipRGC (intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence ...
) react to the light. They interact with each other and send messages to the brain. The rods and cones enable vision. The ipRGCs enable entrainment to the Earth's 24-hour cycle, resizing of the pupil and acute suppression of the pineal
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycl ...
hormone melatonin.
Retina
The retina contains three forms of photosensitive cells, two of them important to vision, rods andcones
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines conn ...
, in addition to the subset of ganglion cells involved in adjusting circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogeno ...
s and pupil size but probably not involved in vision.
Though structurally and metabolically similar, the functions of rods and cones are quite different. Rod cells are highly sensitive to light, allowing them to respond in dim light and dark conditions; however, they cannot detect color differences. These are the cells that allow humans and other animals to see by moonlight, or with very little available light (as in a dark room). Cone cells, conversely, need high light intensities to respond and have high visual acuity. Different cone cells respond to different wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
s of light, which allows an organism to see color. The shift from cone vision to rod vision is why the darker conditions become, the less color objects seem to have.
The differences between rods and cones are useful; apart from enabling sight in both dim and light conditions, they have further advantages. The fovea
Fovea () (Latin for "pit"; plural foveae ) is a term in anatomy. It refers to a pit or depression in a structure.
Human anatomy
*Fovea centralis of the retina
* Fovea buccalis or Dimple
* Fovea of the femoral head
* Trochlear fovea of the fr ...
, directly behind the lens, consists of mostly densely packed cone cells. The fovea gives humans a highly detailed central vision, allowing reading, bird watching, or any other task which primarily requires staring at things. Its requirement for high intensity light does cause problems for astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, g ...
s, as they cannot see dim stars, or other celestial object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often u ...
s, using central vision because the light from these is not enough to stimulate cone cells. Because cone cells are all that exist directly in the fovea, astronomers have to look at stars through the "corner of their eyes" ( averted vision) where rods also exist, and where the light ''is'' sufficient to stimulate cells, allowing an individual to observe faint objects.
Rods and cones are both photosensitive, but respond in different ways to different frequencies of light. They contain different pigmented photoreceptor protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s. Rod cells contain the protein rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction ...
and cone cells contain different proteins for each color-range. The process through which these proteins go is quite similar — upon being subjected to electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic field, electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, inf ...
of a particular wavelength and intensity, the protein breaks down into two constituent products. Rhodopsin, of rods, breaks down into opsin
Animal opsins are G-protein-coupled receptors and a group of proteins made light-sensitive via a chromophore, typically retinal. When bound to retinal, opsins become Retinylidene proteins, but are usually still called opsins regardless. Most pro ...
and retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use retin ...
; iodopsin of cones breaks down into photopsin
Vertebrate visual opsins are a subclass of ciliary opsins and mediate vision in vertebrates. They include the opsins in human rod and cone cells. They are often abbreviated to ''opsin'', as they were the first opsins discovered and are still th ...
and retinal. The breakdown results in the activation of Transducin
Transducin (Gt) is a protein naturally expressed in vertebrate retina rods and cones and it is very important in vertebrate phototransduction. It is a type of heterotrimeric G-protein with different α subunits in rod and cone photoreceptors.
L ...
and this activates cyclic GMP Phosphodiesterase, which lowers the number of open Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel
Cycle, cycles, or cyclic may refer to:
Anthropology and social sciences
* Cyclic history, a theory of history
* Cyclical theory, a theory of American political history associated with Arthur Schlesinger, Sr.
* Social cycle, various cycles in so ...
s on the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
, which leads to hyperpolarization; this hyperpolarization of the cell leads to decreased release of transmitter molecules at the synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ...
.
Differences between the rhodopsin and the iodopsins is the reason why cones and rods enable organisms to see in dark and light conditions — each of the photoreceptor proteins requires a different light intensity to break down into the constituent products. Further, synaptic convergence means that several rod cells are connected to a single bipolar cell
A bipolar neuron, or bipolar cell, is a type of neuron that has two extensions (one axon and one dendrite). Many bipolar cells are specialized sensory neurons for the transmission of sense. As such, they are part of the sensory pathways for smell ...
, which then connects to a single ganglion cell
{{stack,
A ganglion cell is a cell found in a ganglion. Examples of ganglion cells include:
* Retinal ganglion cell (RGC) found in the ganglion cell layer of the retina
* Cells that reside in the adrenal medulla, where they are involved in the ...
by which information is relayed to the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and ...
. This convergence is in direct contrast to the situation with cones, where each cone cell is connected to a single bipolar cell. This divergence results in the high visual acuity, or the high ability to distinguish detail, of cone cells compared to rods. If a ray of light were to reach just one rod cell, the cell's response may not be enough to hyperpolarize the connected bipolar cell. But because several "converge" onto a bipolar cell, enough transmitter molecules reach the synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ...
s of the bipolar cell to hyperpolarize it.
Furthermore, color is distinguishable due to the different iodopsin
Vertebrate visual opsins are a subclass of ciliary opsins and mediate vision in vertebrates. They include the opsins in human rod and cone cells. They are often abbreviated to ''opsin'', as they were the first opsins discovered and are still th ...
s of cone cell
Cone cells, or cones, are photoreceptor cells in the retinas of vertebrate eyes including the human eye. They respond differently to light of different wavelengths, and the combination of their responses is responsible for color vision. Cone ...
s; there are three different kinds, in normal human vision, which is why we need three different primary color
A set (mathematics), set of primary colors or primary colours (see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) consists of colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamu ...
s to make a color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represent ...
.
A small percentage of the ganglion cells in the retina contain melanopsin and, thus, are themselves photosensitive. The light information from these cells is not involved in vision and it reaches the brain not directly via the optic nerve but via the retinohypothalamic tract
In neuroanatomy, the retinohypothalamic tract (RHT) is a photic neural input pathway involved in the circadian rhythms of mammals. The origin of the retinohypothalamic tract is the intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGC), whi ...
, the RHT. By way of this light information, the body clock
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to ...
's inherent approximate 24-hour cycling is adjusted daily to nature's light/dark cycle. Signals from these photosensitive ganglion cells have at least two other roles in addition. They exercise control over the size of the pupil, and they lead to acute suppression of melatonin secretion by the pineal gland
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep, sleep patterns in both circadian rhythm, circ ...
.
Accommodation
depth of field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera.
Factors affecting depth of field
For cameras that can only focus on one object dist ...
of the mammalian eye, an object at one distance from the eye might project a clear image, while an object either closer to or further from the eye will not. To make images clear for objects at different distances from the eye, its optical power needs to be changed. This is accomplished mainly by changing the curvature of the lens. For distant objects, the lens needs to be made flatter; for near objects the lens needs to be made thicker and more rounded.
Water in the eye can alter the optical properties of the eye and blur vision. It can also wash away the tear fluid—along with it the protective lipid layer—and can alter corneal physiology, due to osmotic
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region o ...
differences between tear fluid and freshwater. Osmotic effects are made apparent when swimming in freshwater pools, because the osmotic gradient draws water from the pool into the corneal tissue (the pool water is hypotonic
In chemical biology, tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially-permeable cell membrane. Tonicity depends on the relative concentration of selective membrane-imp ...
), causing edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels t ...
, and subsequently leaving the swimmer with "cloudy" or "misty" vision for a short period thereafter. The edema can be reversed by irrigating the eye with hypertonic
In chemical biology, tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially-permeable cell membrane. Tonicity depends on the relative concentration of selective membrane- ...
saline which osmotically draws the excess water out of the eye.
References
{{vision in animals Vision by taxon eye